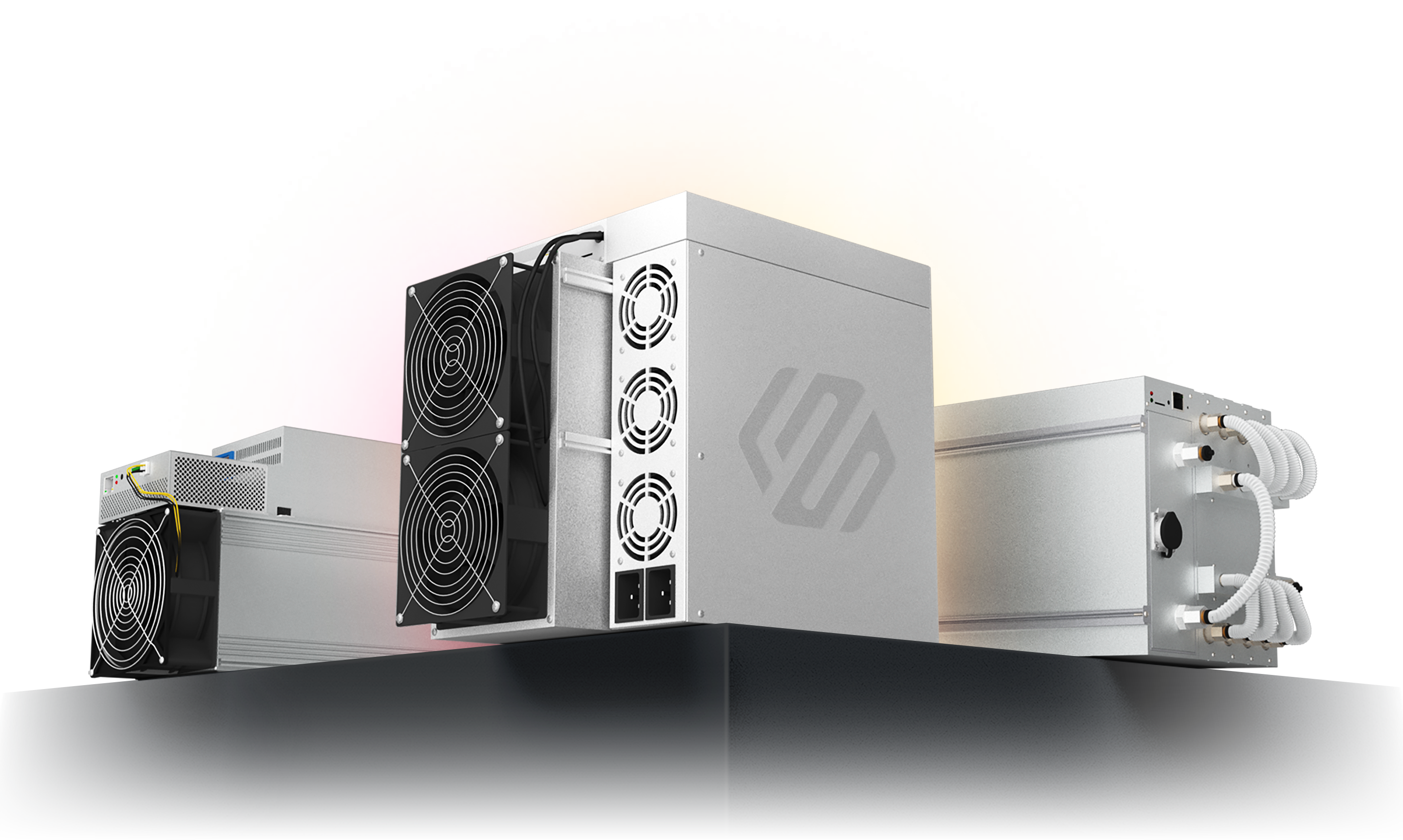













































































Popular Mining Machines
We offer efficient and reliable crypto mining machines, designed specifically for cryptocurrency mining, helping you stand out in the competitive market. Let us be your powerful partner in the journey towards digital wealth.
Real-time Mining Profit
Monitor your mining profits in real time and assess your investment returns.
Learn more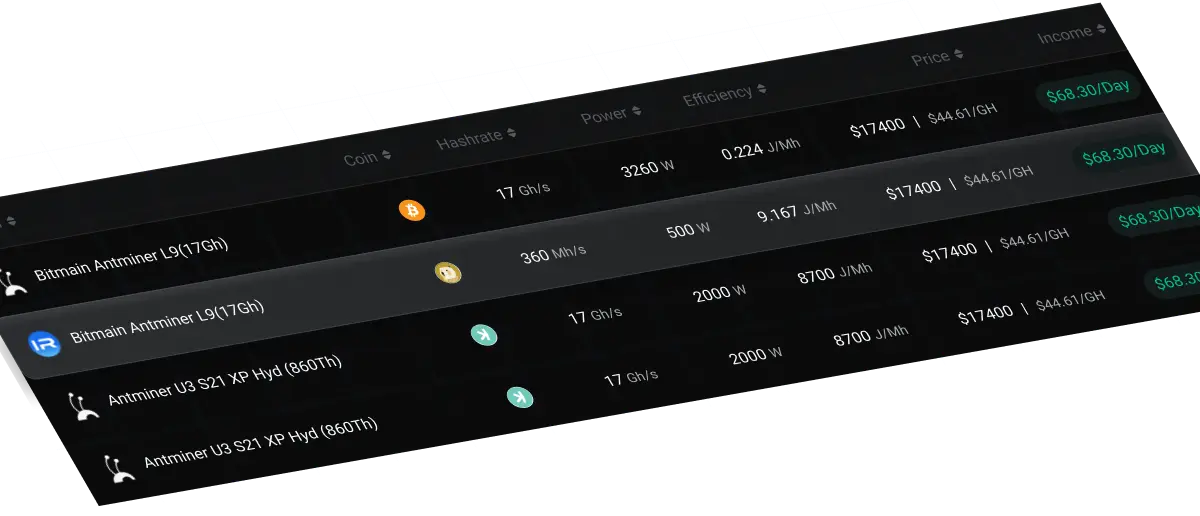

Cryptocurrency Market Trends
Get daily coin market data and stay updated on market trends for better trading decisions.
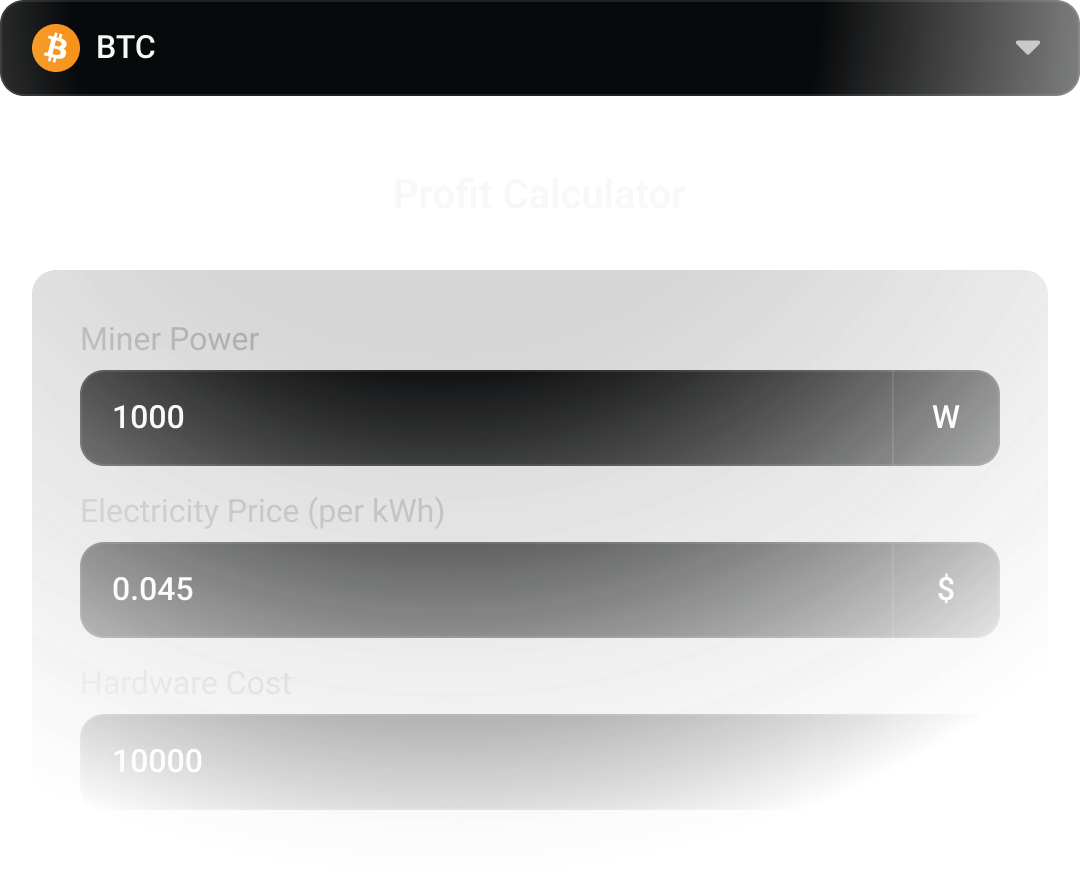
View All CoinsProfit Calculator
Calculate your mining profits with real-time data and accurate power costs estimation.
Why Choose LeedMiner
Leedminer offers top-quality mining equipment at great prices, fast shipping, and lifetime support for a seamless experience.
Reputable Supplier in the Industry
Trusted by thousands of clients worldwide with proven track record in the mining industry.
Providing Complete Mining Solution
One-stop service from equipment selection to setup, maintenance and technical support.
Factory Direct Inventory
Direct partnership with manufacturers ensures authentic products and competitive pricing.
Official Warranty
All products come with official manufacturer warranty for your peace of mind.
Lifetime Customer Support
Professional technical support team available 24/7 to assist you anytime.
Delivery Commitment
Fast and secure worldwide shipping with real-time tracking and insurance.
Recent Exhibitions
Through these exhibition photos, you'll see our technical strength and industry influence in the cryptocurrency mining field, further deepening your trust in our brand.
Mining Disrupt 2025 - North America Cryptocurrency Mining Conference




Our Partners
Trusted by leading companies and organizations in the cryptocurrency mining industry







































Social Partners
Our trusted social media partners, working together to create greater brand value and influence.
News & Events
Stay updated with the latest news...

Fluminer L1 Pro : The Detailed Review
Fluminer L1 Pro enhances mining performance with advanced hardware efficiency.
Read More
What is Cloud Mining ?
Cloud mining rents remote hashrate, eliminating hardware management for users.
Read More
Bitdeer SealMiner A2 Hyd : The Detailed Review
Bitdeer SealMiner A2 Hyd excels with water-cooled, high-performance mining.
Read More
Bitdeer SealMiner A2 Pro Hyd : The Detailed Review
Bitdeer SealMiner A2 Pro Hyd optimizes mining with advanced cooling.
Read MoreLoved by Customers
look what our customers say about us
Ryan Delk
Crypto Mining Consultant
"Leedminer is the most reliable mining machine supplier I've encountered. They not only offer high-quality equipment but also provide comprehensive after-sales support, helping me successfully enter the mining industry."
Sarah Chen
Mining Farm Manager
"The efficiency and stability of Leedminer's machines have exceeded our expectations. Their technical support team is always available and highly knowledgeable."
Michael Thompson
Blockchain Entrepreneur
"What sets Leedminer apart is their commitment to customer success. From equipment selection to ongoing support, they've been an invaluable partner in our mining operations."
Ryan Delk
Crypto Mining Consultant
"Leedminer is the most reliable mining machine supplier I've encountered. They not only offer high-quality equipment but also provide comprehensive after-sales support, helping me successfully enter the mining industry."
Sarah Chen
Mining Farm Manager
"The efficiency and stability of Leedminer's machines have exceeded our expectations. Their technical support team is always available and highly knowledgeable."
Michael Thompson
Blockchain Entrepreneur
"What sets Leedminer apart is their commitment to customer success. From equipment selection to ongoing support, they've been an invaluable partner in our mining operations."
Ryan Delk
Crypto Mining Consultant
"Leedminer is the most reliable mining machine supplier I've encountered. They not only offer high-quality equipment but also provide comprehensive after-sales support, helping me successfully enter the mining industry."
Sarah Chen
Mining Farm Manager
"The efficiency and stability of Leedminer's machines have exceeded our expectations. Their technical support team is always available and highly knowledgeable."
Michael Thompson
Blockchain Entrepreneur
"What sets Leedminer apart is their commitment to customer success. From equipment selection to ongoing support, they've been an invaluable partner in our mining operations."
Ryan Delk
Crypto Mining Consultant
"Leedminer is the most reliable mining machine supplier I've encountered. They not only offer high-quality equipment but also provide comprehensive after-sales support, helping me successfully enter the mining industry."
Sarah Chen
Mining Farm Manager
"The efficiency and stability of Leedminer's machines have exceeded our expectations. Their technical support team is always available and highly knowledgeable."
Michael Thompson
Blockchain Entrepreneur
"What sets Leedminer apart is their commitment to customer success. From equipment selection to ongoing support, they've been an invaluable partner in our mining operations."
Emma Wilson
Cryptocurrency Analyst
"The ROI on Leedminer's equipment has been exceptional. Their transparent approach and professional guidance made our investment decision much easier."
David Park
Mining Pool Operator
"Having worked with various suppliers, Leedminer stands out for their product quality and service reliability. Their after-sales support is unmatched in the industry."
Alexandra Martinez
Digital Asset Manager
"Leedminer's expertise in the mining industry is evident in every interaction. Their equipment performs exactly as promised, and their support team is always ready to help."
Emma Wilson
Cryptocurrency Analyst
"The ROI on Leedminer's equipment has been exceptional. Their transparent approach and professional guidance made our investment decision much easier."
David Park
Mining Pool Operator
"Having worked with various suppliers, Leedminer stands out for their product quality and service reliability. Their after-sales support is unmatched in the industry."
Alexandra Martinez
Digital Asset Manager
"Leedminer's expertise in the mining industry is evident in every interaction. Their equipment performs exactly as promised, and their support team is always ready to help."
Emma Wilson
Cryptocurrency Analyst
"The ROI on Leedminer's equipment has been exceptional. Their transparent approach and professional guidance made our investment decision much easier."
David Park
Mining Pool Operator
"Having worked with various suppliers, Leedminer stands out for their product quality and service reliability. Their after-sales support is unmatched in the industry."
Alexandra Martinez
Digital Asset Manager
"Leedminer's expertise in the mining industry is evident in every interaction. Their equipment performs exactly as promised, and their support team is always ready to help."
Emma Wilson
Cryptocurrency Analyst
"The ROI on Leedminer's equipment has been exceptional. Their transparent approach and professional guidance made our investment decision much easier."
David Park
Mining Pool Operator
"Having worked with various suppliers, Leedminer stands out for their product quality and service reliability. Their after-sales support is unmatched in the industry."
Alexandra Martinez
Digital Asset Manager
"Leedminer's expertise in the mining industry is evident in every interaction. Their equipment performs exactly as promised, and their support team is always ready to help."
Join Our Community
Get the latest news, technical support, and experience sharing through our community.
Contact Support
Our team is ready to answer your questions and provide professional support 24/7.







